The Definitive Technical SEO Audit Checklist
SEO isn’t just about keywords and backlinks. This guide will provide a roadmap to discovering the hidden technical issues that could be holding your website back.
Bookmark this site because our checklist covers all the elements you need for a thorough technical SEO audit.
Crawl Your Website to Get a Lay of the Land
Before I built SiteGuru to automate technical SEO audits, I used tools like Screaming Frog to run crawls. Tools like these two will do what search engine bots do: run over your site, measure relevant metrics, and flag any errors, so you know what’s happening with your website’s SEO.

Crawling your website in SiteGuru - get a score and expand on the details to see specific issues you need to resolve.
Check Your Crawl Budget
If you have a big website (typically in eCommerce), check your crawl budget to ensure you’re not exhausting Google’s resources, causing it to be unable to index changes and newer pages.
- Go to your Google Search Console
- Navigate to Settings in the left-hand sidebar
- Open the “Crawl stats” report
Learn more about your crawl budget.
Check for Immediate Red Flags in Your Technical SEO Audit
Your crawl should show any problems, including errors, indexation problems, manual actions, etc. You’ll prioritize fixing them depending on their ability to impact your website, or - if you use an SEO to-do list tool like Siteguru - the tool will tell you which problems you should tackle first.
SSL Configuration
Your SSL certificate should be configured correctly to verify your website ownership. If you use SiteGuru or another SEO audit tool, it’ll flag issues for you. Otherwise, you can check it with free tools.
Indexation Errors
Has Google indexed all the pages you want to rank? It’s normal not to see your back-end and paginated pages, but check the indexation report for any problems:
- Go to your Google Search Console
- Navigate to “Pages” in the left-hand sidebar
- Check the pages indexed vs. not indexed
If you want to check the indexation status of a specific page, use the free noindex checker.
Learn more about Google coverage statuses (and how to fix them).
404 and 5xx Errors
The indexation report will also show if you have internal links to pages that don’t (or no longer) exist on your website. These waste Googlebots’ resources and affect your user experience score - eliminate them.
If your hosting provider is unreliable, you may see 5xx Errors.
Review Your Core Web Vitals and PageSpeed Insights
User experience is paramount in SEO, so having a slow or poorly structured website can reduce your rankings and traffic. The good thing is that Google has a free PageSpeed Insights test that shows you what’s wrong with your website.
Unfortunately, you’ll have to run the test for each page separately with PageSpeed Insights. SiteGuru runs it for your pages every week.
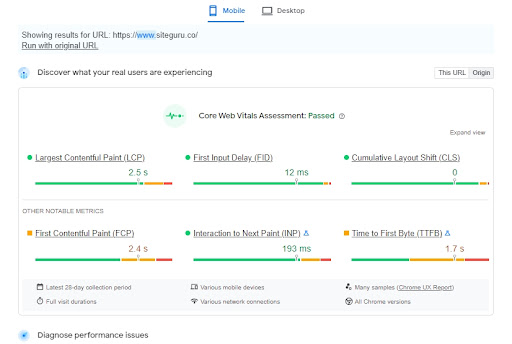
LCP: How Quickly Do Your Pages Load?
Your primary loading metric, the Largest Contentful Paint, shows how quickly the visitors see the critical parts of your website.
Aim to keep your LCP under 2.5 seconds.
FID: How Quickly Does Your Website Respond to User Interactions?
Have you ever clicked a website button only for it to take ages to respond? That’s what the First Input Delay measures. Optimize THE FID for under 100 milliseconds.
CLS: Does Your Website Shift as It Loads?
The Cumulative Layout Shift measures visual stability, i.e., how much your website “moves around” as it loads. Your UX should be pleasant without distracting shifts, so ensure your CLS is under 0.1.
Is Your Website Mobile-Friendly?
All the elements on your desktop site should be available on the mobile version. You can check your pages with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.

I recommend making your website mobile-first, considering how many people exclusively use their phones (especially in B2C).
Image & Asset Compression
Use text, image, and code compression methods to avoid giant files that take a while to load.
For example, you can use the WebP or AVIF formats instead of the JPEG image format.
Not sure if your website compression is enabled? Try the free checker!
Learn more about compression and page speed.
Code Bloat & Minification
A thorough technical SEO audit will help you identify any code bloat problems. For example, you may have unused JavaScript or CSS that inflates your website code, affecting its loading time.
Make sure you minify your JavaScript and CSS and minimize third-party app usage.
Review Your Cache Policy
Caching stores portions of your website’s static (unchanging) content in the browser memory, so the next time the same visitor comes to your website, it’ll load faster.
Make sure your website browser caching is enabled.
Learn more about optimizing Core Web Vitals and Page Speed.
Assess Your Website Structure in Your Technical SEO Audit
Your website structure has two main functions: it helps visitors navigate your website and shows search engines the most important pages. These two functions feed into one another and ultimately affect the user experience (UX) - an essential aspect of SEO.
Without a good user experience, you won’t see high time-on-page, engagement, or conversion metrics. Instead, your visitors will leave your website, sending signals to Google that you haven’t met their intent and causing it to respond by de-ranking your website.
Here’s how to ensure your website structure supports your (technical) SEO efforts:
Is Your Website Hierarchy and Categorization Intuitive?
Your website should be easy to navigate, with your pages neatly organized into categories and sub-categories.
I recommend choosing one of the following website taxonomies:
- Flat taxonomy: Not much branching, simply the homepage and main categories.
Example: SiteGuru -> Features -> Indexation - Hierarchical taxonomy: Categories, sub-categories, and levels. Typically seen on eCommerce websites.
Example: Hiking store -> Equipment -> Hiking backpacks -> Daypacks -> Individual product - Network taxonomy: Your pages are connected by association. You can use it in tandem with a hierarchical website structure.
Example: Website -> Bestsellers -> Jeans + Tote bags - Faceted taxonomy: Usually used in eCommerce, where you supplement the main website’s taxonomy with additional product filters.
Example: Hiking store -> Equipment -> Hiking backpacks -> Daypacks -> Volume + Brand + Recommended use -> Products matching the filters
Learn more about website taxonomy and structures.
Categorization
Categorization is especially important for eCommerce technical SEO because you need to make it intuitive for visitors to browse.
- Every (sub)category should have a purpose.
- Your most important pages should be the closest to the homepage.
- Make sure your sub-category and category pages are internally linked.
Learn more about eCommerce categorization SEO.
Navigation
Your navigation has to emphasize the important pages (at most, two clicks away from the homepage).
Structure your internal links so bots can access other pages using only links. The more internal links a page gets, the higher its perceived priority. (Plus, your link equity will be more evenly distributed when it’s sent to your most important pages, which then share the link juice with other pages through internal links.)
To make your website more mobile-friendly, consider adding breadcrumb navigation.
How to Assess Your URL Structure in a Technical SEO Audit
Your website URLs should be uniform and adhere to the SEO best practices:
- Include the key elements in the URL structure. (See below.)
- All your URLs should follow the same structure.
- Use hyphens rather than underscores.
- Include relevant keywords.
- Remove unnecessary words and numbers.
- Use descriptive instead of numerical permalinks.
Bad URL: example.com/product-12345
Good URL: example.com/great-product-for-audience

Learn more about SEO best practices for URLs.
Duplicate URLs
You might get duplicates if you offer multiple variants of the same product or haven’t implemented faceted navigation properly.
If that’s your case, canonicalize the URLs, i.e., tell Google which page to index and which to ignore.
Learn more about canonical URLs.
Check Your Sitemaps and the Robots.txt File
Ensure you have an up-to-date XML sitemap (a map of all the pages and content on your website) uploaded to the Google Search Console. Google’s bots will use it to get information on the pages they should crawl and index.
Check your current sitemap for any:
- Outdated and deleted pages (remove them from your sitemap)
- Missing pages (add them to your sitemap)

Checking your sitemap in SiteGuru
Image and Other Sitemaps
If you post a lot of images or videos that are important to your business (e.g., eCommerce and product images, photographers, etc.), create separate sitemaps for them. It’ll be easier to manage them and keep the crawl budget in check.
Learn more about creating and updating XML sitemaps.
Review Your Robots.txt File
Your robots.txt file holds all your indexing exclusions.
For example, you don’t want Google to crawl a category tag, paginated blog results, or the access to your back end.
- Make sure your robots.txt file has all the necessary exclusions.
- Create rules to automatically block bots from crawling auto-generated and other pages you don’t want them to crawl (e.g., blog pagination).
- Verify that you aren’t accidentally blocking Google from crawling the pages you want to be crawled.
How to use the robots.txt file.
Check Your Redirects
(Re)move content properly. Your technical SEO audit will uncover any problems with the typical 3xx redirects:
- 301 redirects: permanently moved pages (e.g., products no longer in stock, redirecting to the category page)
- 302 redirects: temporarily moved pages (e.g., product currently unavailable, redirecting to a close variant)
If you have a lot of redirects, create a redirect map to keep track of them.
The complete guide to redirects and SEO.
Audit Your Internal Links
Both visitors and bots will use your internal links to navigate your site, but they also play a role in your link equity (outbound link distribution).
Ensure there are no critical errors:
- Check and fix broken internal links.
- Identify orphan pages (pages that aren’t linked to).
- Ensure your most important pages get enough links from other pages.

A great example of a good internal linking structure by Wordstream.
Structured Data
Structured data allows you to point the finger at specific things on your website and tell the bots: “This is a video. This is a product rating. This is a blog article” through data.
(In some cases, it results in more exciting SERP listings, too.)
- Validate your structured data with a free checker.
- Make sure you implement the relevant Schema types.
- Fix any malfunctioning Schema.
- Add OpenGraph tags for dynamic social sharing posts.
Learn how to add and use Schema and structured data.

Keep an eye on your structured data with SiteGuru
Asset Optimization, Meta Descriptions, and Alt Texts
Optimize your entire site and the details that come with each asset, starting from images.
- Identify images with missing alt texts and add them.
- Make your meta descriptions enticing and add keywords.
- Optimize your page titles.
- Use the right H-tag hierarchy in your posts (H1 as the title, H2 as the main heading, H3 as a sub-heading, etc.).
Grasp the basics of SEO with in-depth guides.
Content Issues You May Find in a Technical SEO Audit
Even though you might think of content as a separate part of your SEO strategy, there are a few technical things that can go bump in the night.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is a common problem for eCommerce websites. If you use faceted navigation, it could automatically generate URLs for searches using different filters.
Make sure you use AJAX faceted navigation and canonicalize the correct pages.
Prevent and fix faceted navigation issues.
Internal Page Competition (Cannibalization)
You'll be cannibalizing both pages' results if you have multiple pages that rank for the same keyword. It could lead to both pages getting de-ranked in the SERPs and your overall website authority suffering.
Decide which page you want to keep, strengthen its content, and modify or redirect the other.
Tackle keyword cannibalization like a pro.
eCommerce Technical SEO
Your eCommerce technical SEO audit will have a lot of items in common with a standard audit. You’ll need structured data, a correct XML sitemap, and meta descriptions.
However, you’ll also need to pay attention to a few other things, including:
- Product feed SEO - Is your store integrated with Google Merchant Center, so your products can appear when searched for?
- Unique product pages - Do your product pages stand out, or is their content similar to other content on your website (or your competitors’ content)?
- Faceted navigation duplication (see the section above) - Use AJAX faceted navigation to prevent generating URLs for filtered searches and exhausting your crawl budget.
- Redirects for temporarily and permanently unavailable products - Deal with products out of stock correctly using 301 and 302 redirects, as well as UX best practices (make it clear that the product is unavailable and direct the visitor to a close variant or the category page).
Learn everything about eCommerce SEO.
International Websites
If you need specific pages (or website versions) for different countries, you’ll need to build the right international SEO foundations.
(Think: Amazon with its localized Amazon.com, Amazon.es, and Amazon.ca variants.)
You can skip this section if you use the same website version for the global audience.
International Website Structure
Make sure you’re using one of the following international website structures:
- Different subfolders
Example: the US website: example.com/en-us, the GB website: example.com/en-gb - Different domains
Example: example.it for Italy, example.es for Spain - Different subdomains
Example: fr.example.com for France, de.example.com for Germany
Typically, the different subfolders approach is the best for SEO because you share SEO results, and the maintenance isn’t as complicated.
Pick the right method with our international website SEO guide.
Hreflang Tags
No matter the method, you’ll likely need to use hreflang tags to specify which country and language you’re targeting with a localized page.
For example, if you have two website versions, you’d specify which is meant for which audience with the following hreflang tags:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="https://www.example.com/en/us">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-ca" href="https://www.example.com/en/ca">
Learn more about using hreflang tags for international SEO.
Website Speed and CDN
The closer your server, the faster the load time. Now, with localized websites, you could purchase servers in other locations to make your website load faster everywhere.
Or you could try a Content Delivery Network (CDN). CDN services have globally distributed servers, so your content is always served from the server closest to the visitor.
This makes your website load super fast, so even if you’re not doing international SEO, you might want to consider a CDN.
What Should Your Technical SEO Audit Tell You?
If you tick all these items off your checklist, your technical SEO audit will help you identify problems and improvement areas. You can do some tasks I mentioned here manually. However, it’s much better to use a tool like SiteGuru, which automatically crawls your website every week and gives you a prioritized SEO to-do list.
But no matter what, don’t skip technical SEO. It will give the rest of your strategy the strong foundations you need to outrank your competition and convert your visitors.


