What is a manual action?
A manual action is a penalty given by Google to your site. It’s bad news for SEO, because it means your site is banned from Google’s index, or that your site will drop significantly for most keywords. Not good.
The site is getting a penalty because Google believes it’s trying to manipulate the search results in a way that goes against the webmaster quality guidelines.
It’s called a manual action because you’re not penalized by an algorithm, but because an actual human being has reviewed your site and thinks it’s manipulative.
Google issues manual actions to fight spammers and other bad actors. By doing so, they aim to keep the quality of the search results at a high level.
How to know if there is a manual action on your site?
No guessing is needed. If you got a manual action, Google tells you in Google Search Console. There’s a dedicated Security & Manual Actions report that lists all manual actions against your site. Normally, that report looks like this:

If you see this message, there are no manual actions against your site. Did your site drop in the rankings? You’ll have to look for other issues or Google updates that might affect your site.
If there is a manual action against your site, the report will show you:
- What type of issue was found
- Which pages are affected. This could be a folder like www.website.com/blog/*, or it could say Affects all pages
- A Request Review button. More on that later.
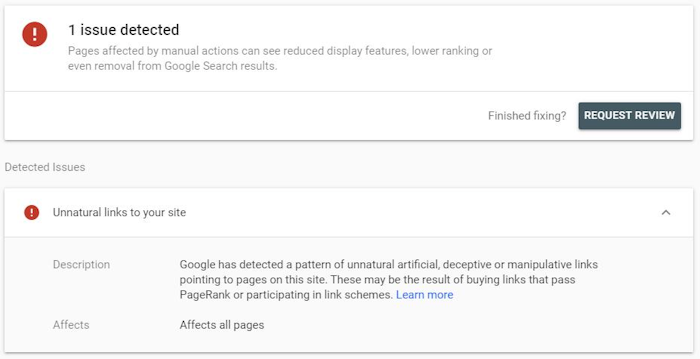
Here’s an example of a manual action for unnatural links:
Manual actions vs. Google updates
A manual action is completely different from a Google update. A manual action only affects your site, whereas a Google update affects lots of sites across the web. A Google update means they change the way sites are ranked, and that may affect your rankings.
In a way it’s better to get a manual action: Google tells you exactly what the issue is and how to fix it. After fixing the issue, you should show up in the SERP again. Contrary, a Google update involves more guesswork and it can be much harder to recover from that.
How to recover from a manual action?
The good news about a manual action is that you’re told what the issue is and how to fix it. The exact fix depends on the type of manual action. If, for example, you got an Unnatural links manual action, you can disavow those links. Did you get a manual action for thin content, you can remove that content.
After you’ve made the required changes, click the Request Review button. Now, you have a so-called reconsideration request pending with Google. They’ll review this manually, and after some time, the manual action will be lifted - if you fixed everything correctly.
Make sure to only place the request after fixing the issue on all the affected pages. Google will provide updates in Google Search Console. I’ve filed a few Reconsideration requests myself and in all cases they were handled within a day.
Spam
Manual actions can include:
- Site abused with third-party spam
- Pure spam
- User-generated spam
Issue
Google found a lot of spammy content on your site. The content is either user-generated (on forums, message boards or the comment section of your blog), or scraped content from other sites.
How to recover
Remove the spammy content. If the content was created by users, you may want to look at extra measures to prevent this spam from coming back in the future. After you’ve fixed the issue, click the Request Review button in Search Console.
Structured data issue
Issue
There is an issue with the structured data on your site. There are a lot of possible issues, but it all comes down to having structured data that is different from the actual content. For example, you could show a 3-star review on your site, with structured data acting as if it is a 5-star review. Other examples are mostly related to misleading JobPosting content. See all the details on Google’s Manual Action page.
I once had a structured data penalty on an e-commerce site. The product page had 3 reviews displayed, and the rest of the reviews were only shown after clicking View All. This is an example of structured data in hidden content.
Don’t worry, you won’t get this action if your structured data is not valid. It’s only applied if it is considered misleading.
How to recover
Make sure your structured data reflects the actual content on your site, and that it is not misleading in any way. If in doubt, just remove the structured data altogether and add it back after you know what the issue is.
Unnatural links to your site
Issue
If you’ve participated in a link scheme or bought a lot of backlinks, you’re likely to get this penalty. Google has strict guidelines regarding links, and this action indicated you haven’t played by the rule.
Have you done nothing wrong? It could be that a mean competitor bought spammy links on your behalf to get you penalized.
How to recover
Either way, disavowing these links is the quickest way to recover. You’ll provide a list of links to Google, and they’ll disavow (ignore) these links. After submitting it, file a review request and you should be fine.
Unnatural links from your site
Issue
Similar to the issue above, but different. In this case, your site seems to have lots of unnatural links that you got paid for. They don’t provide value to the user and Google thinks they are manipulative.
How to recover
You have two options to fix this issue:
- Remove the unnatural links
- Add a no-follow attribute to them
Thin content with little or no added value
Issue
The name same it all. You have many pages that contain hardly any useful content. It can be automatically generated, or low-quality pages in general.
How to recover
If you think the content is of low quality, you should either remove that content or improve its quality so that it becomes useful to your visitors.
If you don’t see any issues with the content, it could be that Google thinks you’ve stolen the content, making it duplicate content. Check if the affected content is available somewhere else on the internet, and submit a reconsideration request after fixing it.
Cloaking
Manual actions can include:
- Cloaking and/or sneaky redirects
- Cloaked images
Issue
Cloaking means you’re showing your users something else than what you’re showing Google. If you have specific logic in your site for search engines (like redirects, showing different images, etc), this can be deceptive.
How to recover
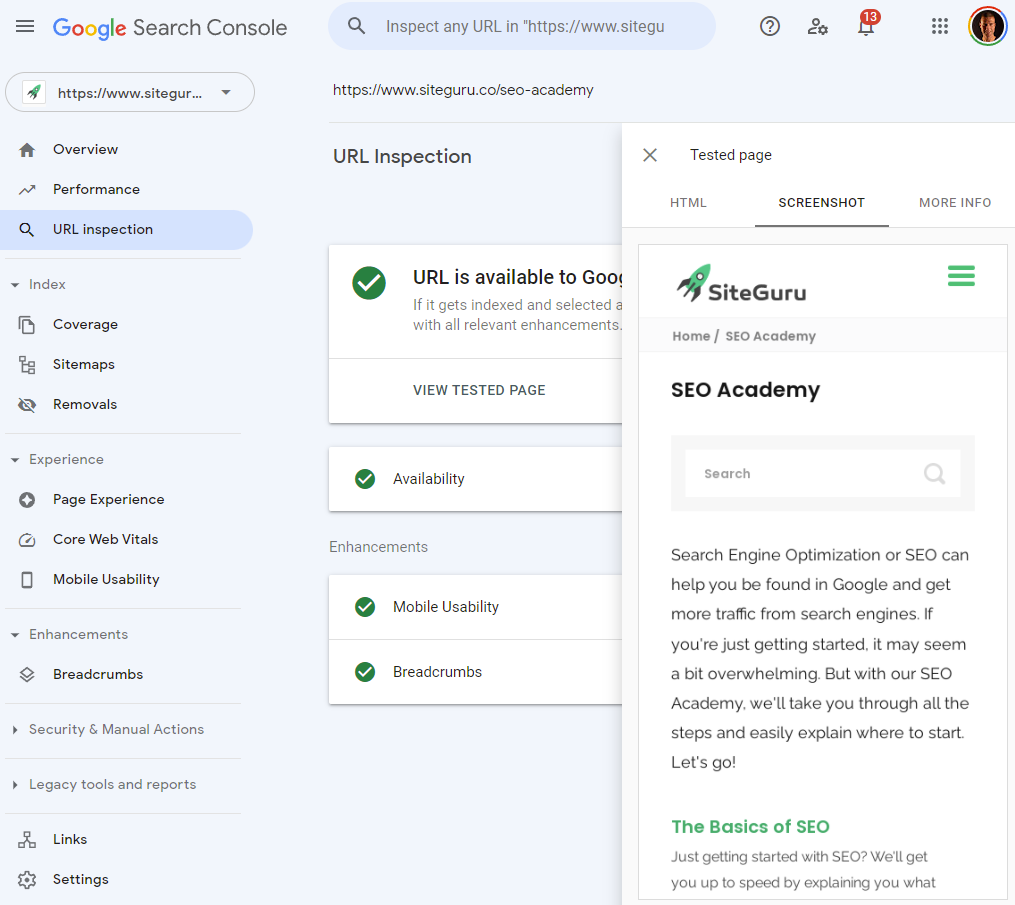
If you’re not sure why Google thinks you’re site uses cloaking, Google Search Console has the Fetch As Google feature to find out.
Go to URL Inspection? Enter the URL ? click Test Live URL —> View tested page. Click Screenshot to see the page as Google sees it. If this is any different from what you see on your screen when visiting the page, that could be cloaked content.
Remove any logic around cloaking, make sure Google sees what your visitors are seeing, and file a Reconsideration request.
Hidden text and/or keyword stuffing
Issue
This can happen when you happen when you're using a certain keyword excessively on a page, in a way that it becomes unnatural to read. Or, even worse, if you have a lot of keyword-optimized text that is not hidden to the visitor.
These are SEO techniques from the past. Consider looking for a new SEO agency if you’ve been tricked into applying these tactics. If you make sure your content is visible and appealing to your visitor, you won’t run into this issue. More about SEO techniques to avoid.
How to recover
Write a text for human beings, and remove any text that is invisible from your code.
AMP content mismatch
Issue
AMP stands for Accelerated Mobile Pages, a content distribution method used by Google to quickly deliver content to mobile browser. With the page experience update, this is no longer relevant, but if you’re using AMP, you may still see this action.
You’ll get this penalty if your AMP version is different from your regular content.
How to recover?
Make sure your regular version of the page and the AMP version are the same.
Sneaky mobile redirects
Issue
This action may arise if you’re redirecting mobile visitors to an entirely different, unrelated website. You obviously won’t get a penalty for redirecting to the mobile version of your website (from example.com to m.example.com, for instance).
How to recover?
I’m not sure why anyone would redirect mobile visitors to an unrelated website, but if you’re doing that, please stop it.
News and Discover policy violations
Issue
If you run a news website, there are specific requirements if you want to be shown in Google news. Any content that is dangerous, misleading, adult-themed or hateful is not allowed. This action will only affect your performance in Google News and Google Discover.
How to recover?
Remove the content that doesn’t meet the requirements for Google news and file a reconsideration request.
Conclusion
Google can apply a manual action to your site, which has a very serious negative impact on your visibility in Google. You get this penalty because you didn’t play by Google’s rules.
You’ll see the details about the manual action in Google Search Console, including details about how to fix the issue. After fixing it, you can file a reconsideration request, which Google will review. If all went well, your site should be back in Google’s index shortly.


