You probably noticed two schools of thought if you researched domain names and SEO. Some say your domain name can profoundly affect your rankings. In contrast, others claim that your domain name can’t possibly affect your SEO.
The truth is somewhere in the middle. And with that in mind, let’s start by dispelling myths and answer the question once and for all: can your domain name affect your SEO?
SEO Domain Name Myths: Busted!
Myth: Domain Name Is a Ranking Factor
Truth: No, your domain name isn’t a ranking factor.
One of the most common myths you might have heard is that using keywords in your domain name could give you a boost in rankings.
Years ago, website owners bought exact match domains. For example, if you sold hiking gear, you’d have bought a domain with the keyword in the name (e.g. brandxyzhiking.com). Now, exact match domains make no difference and they’re not a ranking factor. Google’s John Mueller confirmed as much as far back as 2020.
Keep in mind, though, that the only instance where your domain name might impact your search ranking is with purely navigational searches. For example, if someone searches for your website with your domain name as the search query.

Myth: Domain Age Can Affect Your SEO
Truth: Domain age can’t affect your SEO.
The next myth that needs busting is that your domain’s age can affect your search rankings. This simply isn’t true. In fact, several Google employees have confirmed the opposite.
If you buy an aged domain in your industry, you could inherit bad backlink profiles, low-quality content, and penalties.
So, there’s no need to go hunting for a second-hand domain that matches your brand, but this myth likely originated from the fact that it takes a while to increase your Domain Authority.
Myth: Domain Registration Impacts SEO
Truth: Your domain registration period doesn’t affect your SEO
Another myth you’ll often hear is that the longer you register your domain name, the better it will perform SEO-wise. In other words, your website will feature higher in the search results if you register your domain name for three years, compared to only one.
This makes no sense. How much you pay for your domain upfront is between you and your domain name provider.
Google has also confirmed that it doesn’t consider domain registration length as a ranking factor.
However, it uses a change in domain ownership as a ranking factor, especially if you make significant changes like changing the domain name or scrapping the majority of the content.
If you don’t plan on changing the domain name, try to stay on the same hosting server (to avoid slowing down the site) and keep the same WhoIs domain owner.
If you plan to change the domain name, create 301 redirects to new pages and get your backlinks updated with the website’s new URLs. Create a new sitemap, update Google Analytics, and verify the ownership change in the Google Search Console by adding the website.
Myth: Domain Authority Affects Your Ranking
Truth: Domain Authority doesn’t affect your ranking - backlinks do
You might have read that your website’s domain authority impacts your SERP position. The thing is, domain authority is a metric developed by Moz that predicts how well a website will do in the search rankings compared to other sites.
The same goes for Ahrefs’ Domain Rating (DR). While it’s useful as a gauge of your link-building efforts, Google doesn’t officially use it.
As such, it does not affect SEO.
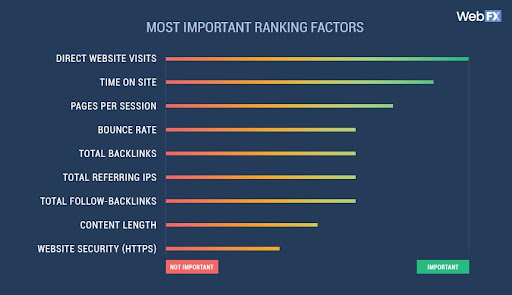
Source: WebFX
We mainly use it in SEO conversations because, among other factors, Moz’s DA looks at your backlink profile.
Since Google uses links to understand your website, DA is a good proxy for understanding how your website compares to others in your niche.
Myth: Top-level domains have a direct impact on SEO
Truth: Top-level domains no longer affect your SEO
The final myth is that your top-level domain or domain extension gives you better search engine rankings. Think of top-level domains as identifiers; they give bots pointers about the nature or location of your website.
For example, .edu domains identified educational institutions. .gov is a sponsored domain, reserved for the use of the US government.
While, in the past, .com domains provided a definite SEO advantage because they allowed bots to easily identify what the website is about, it’s no longer the case. Google now treats all non-local domains the same.
As such, the Google algorithm will treat your site the same, whether it has a .com, .net, or any other non-local domain.
Why Is Your Domain Name Important If It Doesn’t Affect Your SEO?
Your domain name may not affect your SEO directly, but it can affect it indirectly.
Your domain name defines your brand and lets users know who you are, which, in turn, creates trust and authority.
As the right domain name shows professionalism, it adds credibility to your site, so the right name can give you an edge over your competitors. With more trust and credibility, more searchers will click on your website’s link in the SERPs.
As a result, your site’s click-through rates and on-page engagement will improve. And as these are direct ranking factors, your domain name indirectly impacts your site’s SEO.
How to Choose the Right Domain Name
Now that you’ve seen to what extent your domain name impacts your SEO, let’s take a look at how you can choose the right option:
Always Go for a Brandable Domain Name
You should always go for a brandable domain name. It’s simple, unique, easy to remember, and, vitally, makes you stand out from the crowd.
So, think “www.coca-cola.com” instead of “www.bestsoftdrinkintheworld.com.”
Keep Your Domain Name Short
Considering the above, you’ve probably also gathered that you should keep it short. Short domain names are easy to pronounce, easy to type, and easy to remember.
So, “www.apple.com” is good. “www.wesellthebestcomputersintheworld.com” - not so much.
Make It Memorable
Make sure your customers can remember and find you online by making your domain name memorable.
If you do, your customers will soon bypass search engines and type your domain name directly into their browsers’ address bars.
And, when searching, they’ll recognize you in a sea of competitors.
Use Top-Level Domains
Finally, try to get a top-level domain for your website. Even though we said that domain name is not a ranking factor, it is a psychological factor for searchers.
Would you rather click on a domain name that ends with .com or .xyz?
Top-level domains like .com and .net are the most common and popular, and using one will add a flair of credibility to your site.
The Verdict: Your Domain Name Indirectly Affects Your SEO
While your website’s domain name doesn’t directly impact your site’s SEO, it does indirectly affect how well your site performs in search rankings.
Remember: searchers want credibility and opt for domain names that are short, memorable, and trustworthy.
And if you’re unhappy with your rankings, don’t blame your domain name. In a sea of ranking factors, it affects your SEO the least. Instead, grab a free website SEO audit and find out exactly what you need to improve.


